Science Glossary
Science Glossary
Hi, my name is Savera Botros and I study in Science at Montmorency College. This is my third semester studying in this program. Science is a program in which you have a lot of chemistry, biology and physics to do. To enter this program you should have done enriched science and enriched mathematics. The Science program is a program that lasts two years or four semesters. I am writing this glossary to help people that don't know a lot of science terms. I wish this glossary will help you know more about science and my program. To create this glossary, I used Google, Google translate, Wikipedia, and Lextutor.
- activation energy
- noun
- The minimum quantity of energy which the reacting species must possess in order to undergo a specified reaction.
- Example: There is a variation of k with temperature, Arrhenius in 1889 found a relationship that governs this whole concept: where A is the pre-exponential (frequency) factor, E is the activation energy and R the molar gas constant.
- en: énergie d'activation

- alkane
- noun
- Any of the series of saturated hydrocarbons including methane, ethane, propane, and higher members.
- Example: The spectrum also contained the expected alkane C-H and C-C bonds within their predicted areas of ~ 2850-2960cm -1 and ~750-1100cm -1 .
- en: hydrocarbure

- alkene
- noun
- Any of the series of unsaturated hydrocarbons containing a double bond, including ethylene and propylene.
- Example: Although this ligand is not enantiomeric it acts as though it were in the dehydoxylation step, attacking the alkene from the top face.
- en: alcène

- alkyne
- noun
- Any of the series of unsaturated hydrocarbons containing a triple bond, including acetylene.
- Example: The alkyne functional group is the carbon-carbon triple bond. In alkene radicals proton abstraction to an alkyne is preferred.
- en: alcyne

- allele
- noun
- One of two or more alternative forms of a gene that arise by mutation and are found at the same place on a chromosome.
- Example: The diagram demonstrates Mendel's genetic crosses of Pisum sativum indicating the inheritance of characteristics through alleles. If an allele is dominant then its characteristic will always appear in the phenotype. Recessive alleles only appear in the phenotype if they are homozygous.
- en: allèle

- antigen
- noun
- A toxin or other foreign substance which induces an immune response in the body, especially the production of antibodies.
- Example: The antibodies resistance to acidic conditions and pepsin degradation is yet to be confirmed, it was reported that inactivated of the antibody occurred at pH3 due to a major conformational change in its structure lowing the antigen binding affinity.
- en: antigène

- biomass
- noun
- The total mass of organisms in a given area or volume.
- Example: Kingsmead primary school in Cheshire has been built with solar panels in the roof, heating powered by biomass, and a rainwater recovery system.
- en: biomasse
- chromatin
- noun
- The material of which the chromosomes of organisms other than bacteria (i.e., eukaryotes) are composed. It consists of protein, RNA, and DNA.
- Example: In this proposal the centromeric chromatin coils, with increased scaffold attachment.
- en: chromatine

- covalence
- noun
- Valence characterized by the sharing of electrons.
- Example: Moreover, a covalent bond between two highly electronegative elements will clearly be strong.
- en: covalence

- cytosol
- noun
- The fluid portion of the cytoplasm exclusive of organelles and membranes.
- Example: It is a cytosol enzyme specific to the liver, a rise as seen here only occurs in liver disease.
- en: cytosol
- dehydration
- noun
- In chemistry, a dehydration reaction is a chemical reaction that involves the loss of water from the reacting molecule or ion.
- Example: Polyphenol oxidase cause browning of the food stuffs during storage of the freezing or dehydration products by transforming the polyphenol compounds existing abundant in the fruits into brown colored substances.
- en: déshydratation

- dissection
- noun
- To separate into pieces : expose the several parts of (something, such as an animal) for scientific examination dissect an earthworm dissecting flowers. 2 : to analyze and interpret minutely dissect a problem. intransitive verb. : to make a dissection.
- Example: Be cautious of contra-indications such as aortic dissection, head injury, multiple trauma or recent surgery.
- en: dissection

- ecological niche
- noun
- In ecology, the term “niche” describes the role an organism plays in a community. A species' niche encompasses both the physical and environmental conditions it requires (like temperature or terrain) and the interactions it has with other species (like predation or competition).
- Example: Consequently, the species are of medium size, lightly built, slender and long limbed, all of which means they are perfectly adapted to moving quickly in their present ecological niche.
- en: niche écologique

- ecosystem
- noun
- A biological community of interacting organisms and their physical environment.
- Example: The sustainability of the global ecosystem has been problematized and defined in international law according to the perception of those who rule it.
- en: écosystème

- endocytosis
- noun
- The taking in of matter by a living cell by invagination of its membrane to form a vacuole.
- Example: Eukaryotes were rather good at endocytosis as it relieved them of the need to evolve beyond the simple forms of glycolysis for energy generation 2.
- en: endocytose

- enthalpy
- noun
- A thermodynamic quantity equivalent to the total heat content of a system. It is equal to the internal energy of the system plus the product of pressure and volume.
- Example: The enthalpy difference of DFT calculations by Ebmeyer and MMX are within 1.43 kcal mol -1 of each other, however both are approximately 5 kcal mol -1 away from experimental enthalpies.
- en: enthalpie

- enzyme
- noun
- A substance produced by a living organism which acts as a catalyst to bring about a specific biochemical reaction.
- Example: The first of the modification and most common is acetylation by the enzyme acetyltransferase (HAT). This enzyme adds an acetyl group to lysine residues which neutralises its positive charge therefore altering the net charge of the protein.
- en: enzyme

- exocytosis
- noun
- A process by which the contents of a cell vacuole are released to the exterior through fusion of the vacuole membrane with the cell membrane.
- Example: This calcium entry then triggers exocytosis of the presynaptic vesicles.
- en: exocytose

- genotype
- noun
- The genetic constitution of an individual organism.
- Example: Where females disperse a wide distribution of the male genotype across overlapping ranges may result.
- en: génotype

- heterozygous
- noun
- Having two different alleles of a particular gene or genes.
- Example: A rare heterozygous condition of blisters and urticarial lesions on the back or extensor surfaces.
- en: hétérozygote

- homozygous
- noun
- Having two identical alleles of a particular gene or genes.
- Example: He observed that the disease was prevalent in certain families and concluded that affected people are homozygous for a gene which causes the disease.
- en: homozygote

- hydrolysis
- noun
- The chemical breakdown of a compound due to reaction with water.
- Example: Since the development of this chemical hydrolysis a range of semi-synthetic cephalosporins have been synthesised.
- en: hydrolyse

- ionization
- noun
- Ionization, in chemistry and physics, any process by which electrically neutral atoms or molecules are converted to electrically charged atoms or molecules.
- Example: Recent successful experiments have led to control of molecular ionization and dissociation, atomic and molecular fluorescence and passage of currents in semiconductors.
- en: ionisation

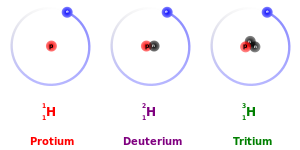
- isotope
- noun
- Any of two or more species of atoms of a chemical element with the same atomic number and nearly identical chemical behavior but with differing atomic mass or mass number and different physical properties.
- Example: Moreover, the structure of article is well-planned, and also main arguments and isotope results are highlighted clearly. However, it might be preferred that the application of scatter gram with valuable isotope results.
- en: isotope
- mitosis
- noun
- A type of cell division that results in two daughter cells each having the same number and kind of chromosomes as the parent nucleus, typical of ordinary tissue growth.
- Example: As the first cell cycle takes place the levels of SKN-1 increase in the P 1 nucleus but not in AB, the AB and P 1 cell both enter mitosis and their daughters contain equal amounts of SKN-1.
- en: mitose

- phagocytosis
- noun
- The ingestion of bacteria or other material by phagocytes and amoeboid protozoans.
- Example: Interaction of Legionella pneumophila with Acanthamoeba castellanii: uptake by coiling phagocytosis and inhibition of phagosome-lysosome fusion.
- en: phagocytose

- phenotype
- noun
- The set of observable characteristics of an individual resulting from the interaction of its genotype with the environment.
- Example: If an allele is dominant then its characteristic will always appear in the phenotype.
- en: phénotype

- photon
- noun
- A particle representing a quantum of light or other electromagnetic radiation. A photon carries energy proportional to the radiation frequency but has zero rest mass.
- Example: The photon appears to travel through both slits at the same time, but when observed, it is a point particle.
- en: photon

- refraction
- noun
- The fact or phenomenon of light, radio waves, etc. being deflected in passing obliquely through the interface between one medium and another or through a medium of varying density.
- Example: As ultrasound is a wave it experiences refraction at the interface between two materials of different densities.
- en: réfraction

- ribonucleic acid
- noun
- Ribonucleic acid, a nucleic acid present in all living cells. Its principal role is to act as a messenger carrying instructions from DNA for controlling the synthesis of proteins, although in some viruses RNA rather than DNA carries the genetic information.
- Example: Next the DNA is analysed, followed by RNA, and it's homology to bacterial RNA.
- en: acide ribonucléique

Comments
Post a Comment